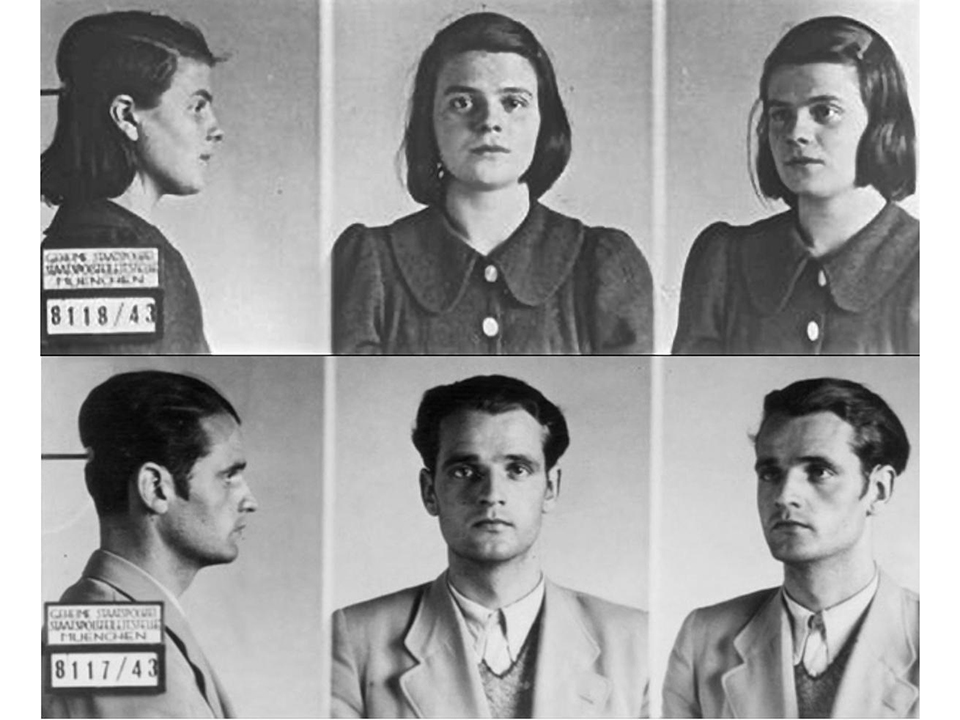
Operation Eiche – the mission Winston Churchill described as “one of great daring“.
1943 was a bad year for the Italian dictator, Benito Mussolini. His hopes of holding North Africa had been dashed, his decision to send Italian troops to help Hitler fight the Russians on the Easter Front was a disaster, and the Allies had landed in Sicily leaving Italy vulnerable in the south. To cap it all, the Allies bombed Rome on 19th July, damaging two of Rome’s airports as well as reducing parts of the ancient Basilica of Saint Lawrence to rubble.
Although Mussolini was a dictator he did not hold the supreme power that his friend, Adolf Hitler, had in Germany. Italy still had a king and a council with the power to remove Mussolini, and by July 1943 they had had enough. On 24th July the Grand Council passed a vote of no-confidence in their leader; Il Duce was summoned to the palace the next day, where King Victor Emmanuel told him that he was to be replaced by Marshal Badoglio. Mussolini must have been stunned when the king told him that ‘Italy has gone to bits. The soldiers don’t want to fight any more. At this moment you are the most hated man in Italy.’ The dictator, who had been in power since 1922, was further stunned to find himself immediately arrested on the orders of the monarch.
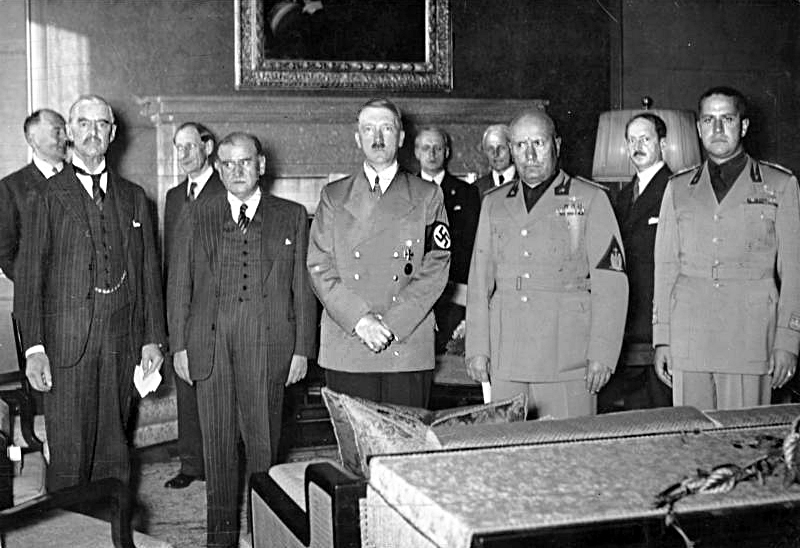

The fall of Mussolini was also a shock to Hitler, who was afraid that Italy would now change sides and support the Allies against him. The only solution was to annex Italian territory and rescue Mussolini. This would not prove as easy as he might have thought as the Italians constantly kept their prisoner on the move, so Hitler appointed Kurt Student to plan a rescue attempt – codenamed Operation Eiche – whilst Hauptsurmfuhrer Otto Skorzeny was sent to Italy to find out where Mussolini was being held. Hitler made the importance of the mission very clear when he told Skorzeny ‘Mussolini, my friend and our loyal comrade in arms, was betrayed yesterday by his king and arrested by his own countrymen. I cannot and will not leave Italy’s greatest son in the lurch. To me the Duce is the incarnation of the ancient grandeur of Rome. Italy under the new government will desert us! I will keep faith with my old ally and dear friend; he must be rescued promptly or he will be handed over to the Allies.’
Skorzeny had been wounded by shrapnel in the back of the head in 1942; when he recovered from his injury he was assigned a job on Hitler’s staff where he was developing commando warfare. In early September, with the use of intercepted radio transmissions, he finally discovered that the deposed dictator was being held in the Hotel Campo, a ski resort in the Apennine Mountains of southern Italy. Unfortunately for Skorzeny, any rescue attempt had to be briefly put on hold as Italy capitulated to the Allies on 8th September and German focus was on taking control of parts of Italy; but the mission could not be delayed for too long in case Mussolini was handed over to the enemy by the Italian government, so planning went ahead, and the rescue attempt took place on 12th September, led by Major Mors.
Mors’s plan was for 12 gliders transporting 3 platoons of Luftwaffe airborne troops and 1 platoon of SS men to land in an open area close to the hotel; at the same time, troops in 20 vehicles would take on the 100 guards at the lower cable-car station and so completely cut off the hotel higher up the mountain. The lower operation went smoothly, and was completed at 14.00 as the gliders (reduced from 12 to 10) came in to land 5 minutes later. To their dismay, the ‘open field’ which had been observed in reconnaissance photographs turned out to be a stretch of steep and rocky ground, causing one of the gliders to crash.
But this crash did not hold up the operation and, within minutes of landing, the Italians’ radio equipment had been put out of action; the guards (100 men at the hotel) appeared confused and did nothing to oppose the attacking Germans – after all, the commando forces had recently been their allies, and the prisoner they were holding was their former commander-in-chief. Skorzeny quickly took advantage of their confusion and raced to Mussolini’s room where he declared “Duce, the Führer sent me to free you”, to which Mussolini replied “I knew that my friend Adolf Hitler would not have abandoned me!”
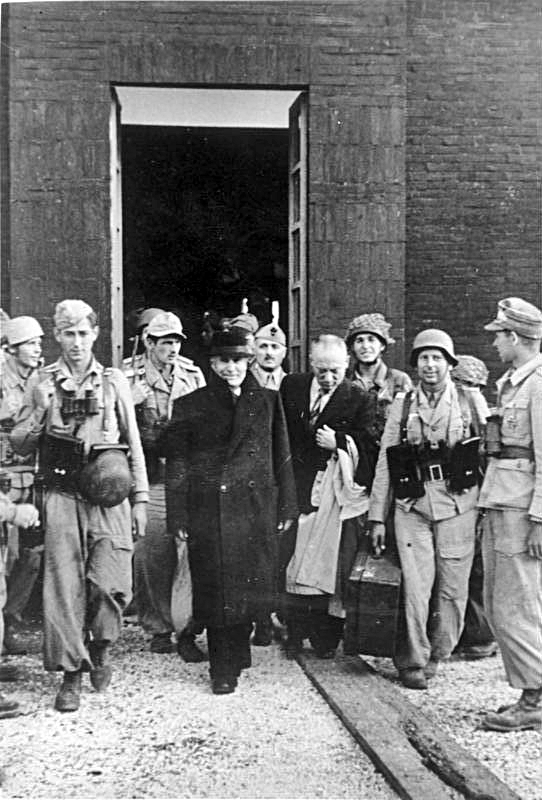
Whilst there had been a short fire-fight when the Germans took the lower cable-car station, the entire operation at the Hotel Campo itself was conducted without a shot being fired. Photographs were taken of a smiling Mussolini with his rescuers, and even some of the Italians who should have been guarding him grinneded happily as they had their photographs taken with their attackers. Il Duce was now the guest of the Germans, and his extraction was imminent.
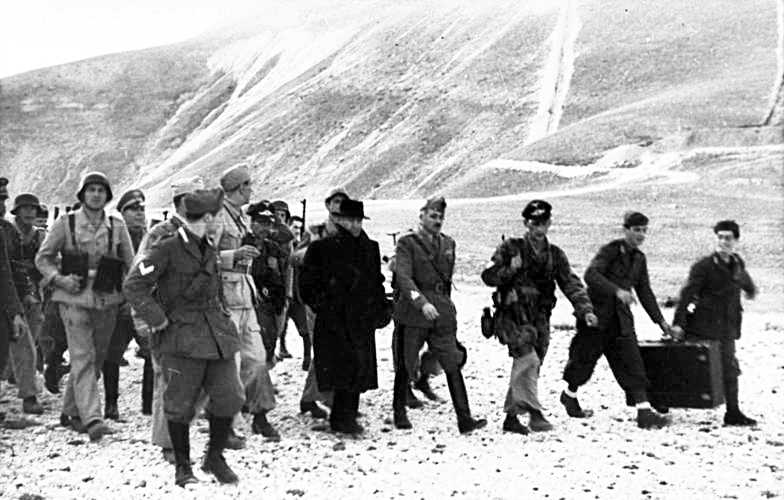

A Fieseler Fi 156 Short-Take-Off-and-Landing plane survived a tricky landing on the rocky strip to pick up its passenger. On take-off there was a frightening moment as the nose of the overloaded Fieseler dipped and the plane plunged down towards the valley floor, but the pilot was finally able to regain control and the deposed dictator began his flight to freedom, changing planes at Pratica di Mare before continuing on to Germany via Vienna. As the plane disappeared into the distance, the gliders which had been used in the raid were destroyed and the German troops took the cable-car down the mountain where they made good their escape.
Mussolini arrived at Hitler’s Wolf’s Lair headquarters, near Rastenburg, on 15th September. The Fuhrer was shocked to see how much weight his old friend had lost since their last meeting, but was glad that his fellow fascist leader was safe. Eleven days later Hitler set up Mussolini as leader of the Salo Republic in northern Italy, but the writing was on the wall for the man who was now hated by the people he once led. On 27th April 1945 Mussolini and his mistress, Clara Petacci, were captured by Italian partisans as they tried to escape from the advancing Allies. The following day he was executed by a firing squad and his body, with that of his mistress and their supporters, was hung by the feet from the roof of an Esso petrol station in Milan.

The popular leader who had led Italy to war, and later been rescued in what Churchill described as a mission of “great daring”, had finally received what the majority of Italian people felt were his just deserts.
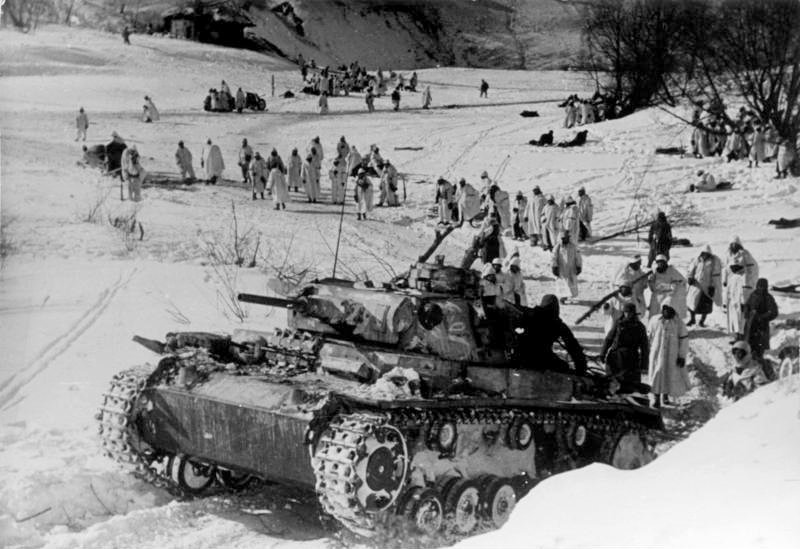
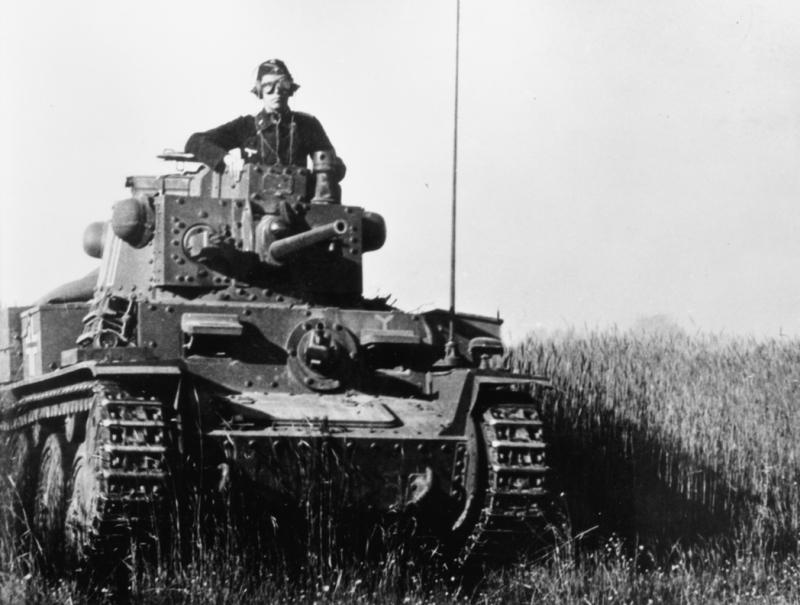







































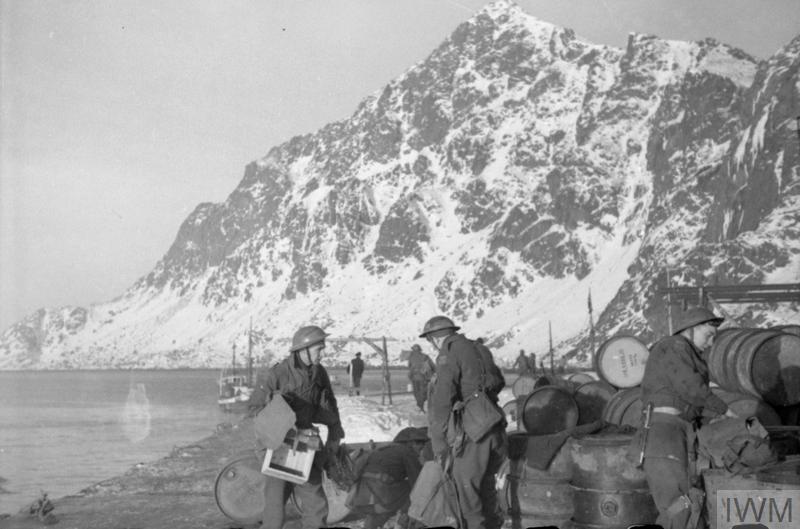
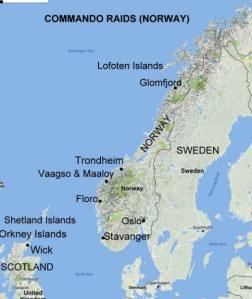 Norway had declared herself neutral at the outbreak of war in 1939, but the country’s strategic position meant that both Britain and Germany had an interest in what was happening there. In particular, the port of Narvik was important to the Germans as it allowed passage through the North Sea for the iron ore which the Nazis obtained from Sweden thus avoiding the Baltic Sea, parts of which regularly froze during the winter months. Almost as important for the Germans as this sea route, if not more so, was the fish oil which was produced in huge quantities in Norway. Why fish oil, you ask? Well, surprisingly, it was used to produce glycerin, which was then used to make nitroglycerin – a major component of dynamite.
Norway had declared herself neutral at the outbreak of war in 1939, but the country’s strategic position meant that both Britain and Germany had an interest in what was happening there. In particular, the port of Narvik was important to the Germans as it allowed passage through the North Sea for the iron ore which the Nazis obtained from Sweden thus avoiding the Baltic Sea, parts of which regularly froze during the winter months. Almost as important for the Germans as this sea route, if not more so, was the fish oil which was produced in huge quantities in Norway. Why fish oil, you ask? Well, surprisingly, it was used to produce glycerin, which was then used to make nitroglycerin – a major component of dynamite.
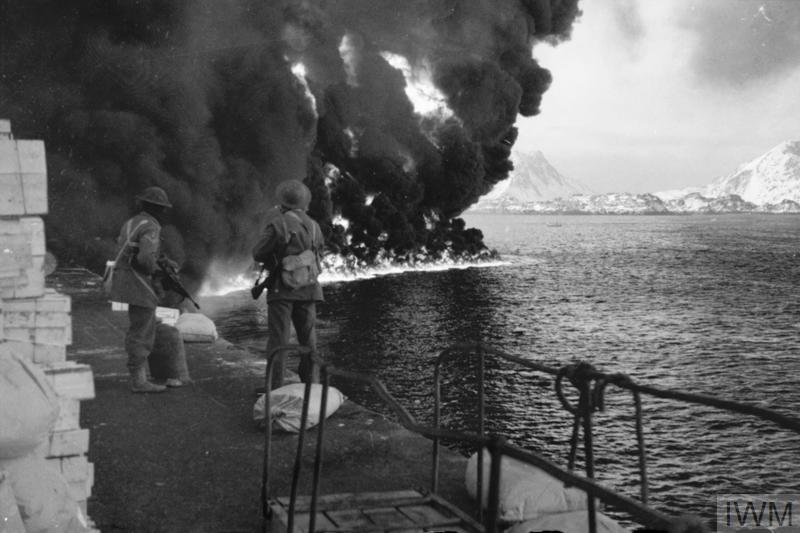
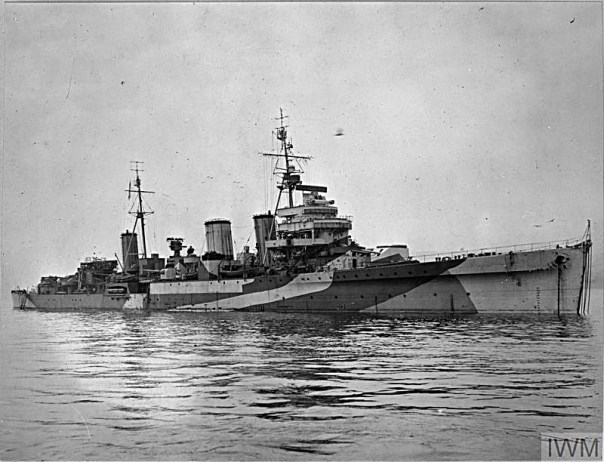
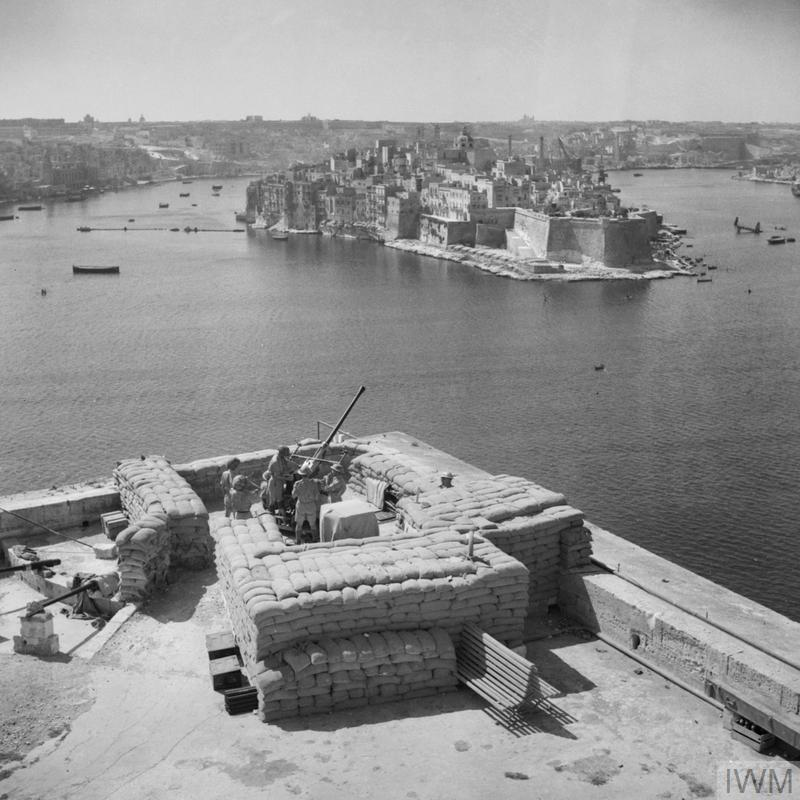





























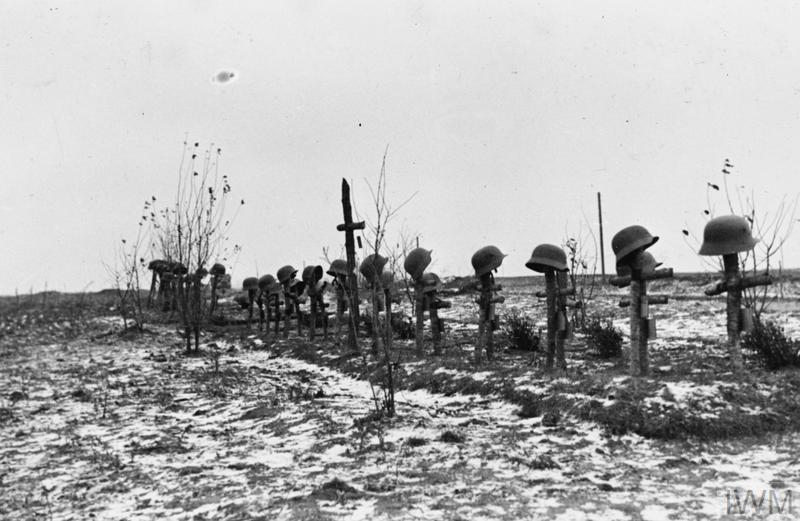
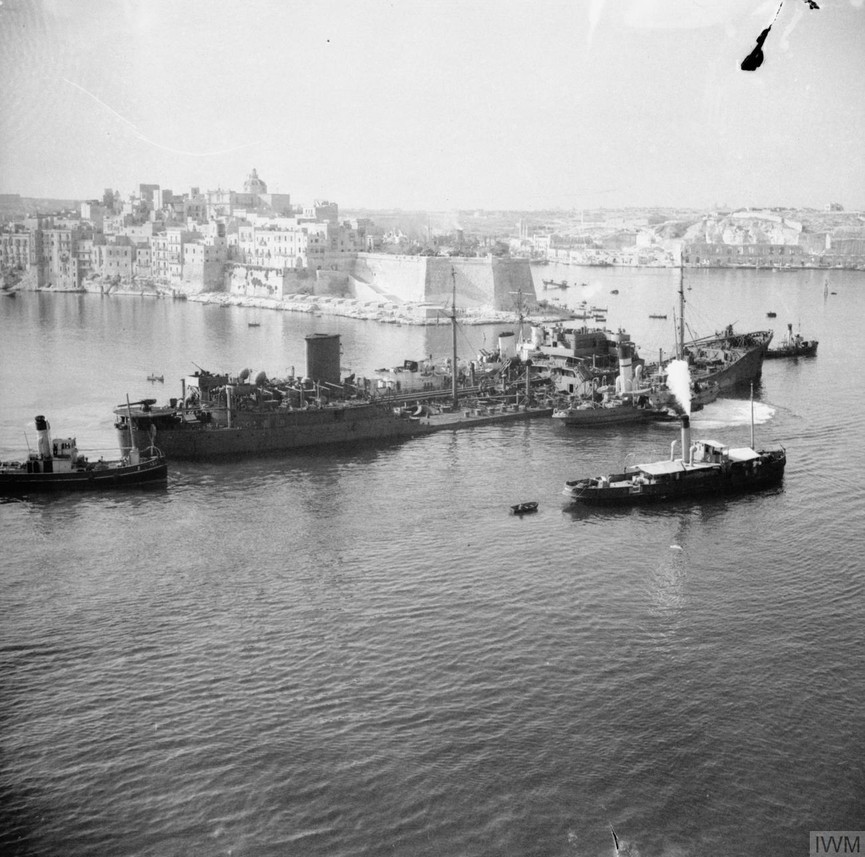
 The British success was, however, short lived as the German aircraft returned to Sicily in December and a second siege of Malta began. As 1941 turned to 1942 the convoys carrying supplies to Malta suffered huge losses of ships and crews – between February and June less than 8% of British ships reached port and unloaded their cargo. The bombing of the island was so intense that civilians were forced to seek shelter in caves and tunnels which they dug into the limestone rock despite the lack of suitable equipment or any skilled miners. The demand for shelters was huge and those that were available were frequently overcrowded. The insanitary conditions inside the shelters led to epidemics of dysentery, typhoid and tuberculosis among an already malnourished population.
The British success was, however, short lived as the German aircraft returned to Sicily in December and a second siege of Malta began. As 1941 turned to 1942 the convoys carrying supplies to Malta suffered huge losses of ships and crews – between February and June less than 8% of British ships reached port and unloaded their cargo. The bombing of the island was so intense that civilians were forced to seek shelter in caves and tunnels which they dug into the limestone rock despite the lack of suitable equipment or any skilled miners. The demand for shelters was huge and those that were available were frequently overcrowded. The insanitary conditions inside the shelters led to epidemics of dysentery, typhoid and tuberculosis among an already malnourished population.









 Three days after the plane was shot down the New York Times reported that “It was believed in London that the Nazi raiders had attacked on the outside chance that Prime Minister Winston Churchill might be among the passengers.” When secret files about Ultra (the Allies’ secret Nazi code-breaking capabilities) were finally made public decades after the Second World War it was learned that the British had known in advance that the Germans assumed Churchill was on Flight 777 and so might target the plane. It was obviously vital for the war effort that Ultra could not be compromised and so the intelligence was not passed on to the Portuguese authorities or the airline. When Churchill wrote his history of the war he fed the flames of the mistaken-identity thesis when he referred to Leslie Howard’s death as one of “the inscrutable workings of fate.”
Three days after the plane was shot down the New York Times reported that “It was believed in London that the Nazi raiders had attacked on the outside chance that Prime Minister Winston Churchill might be among the passengers.” When secret files about Ultra (the Allies’ secret Nazi code-breaking capabilities) were finally made public decades after the Second World War it was learned that the British had known in advance that the Germans assumed Churchill was on Flight 777 and so might target the plane. It was obviously vital for the war effort that Ultra could not be compromised and so the intelligence was not passed on to the Portuguese authorities or the airline. When Churchill wrote his history of the war he fed the flames of the mistaken-identity thesis when he referred to Leslie Howard’s death as one of “the inscrutable workings of fate.”




